What is a Wedge Brake Chamber and how does it function?
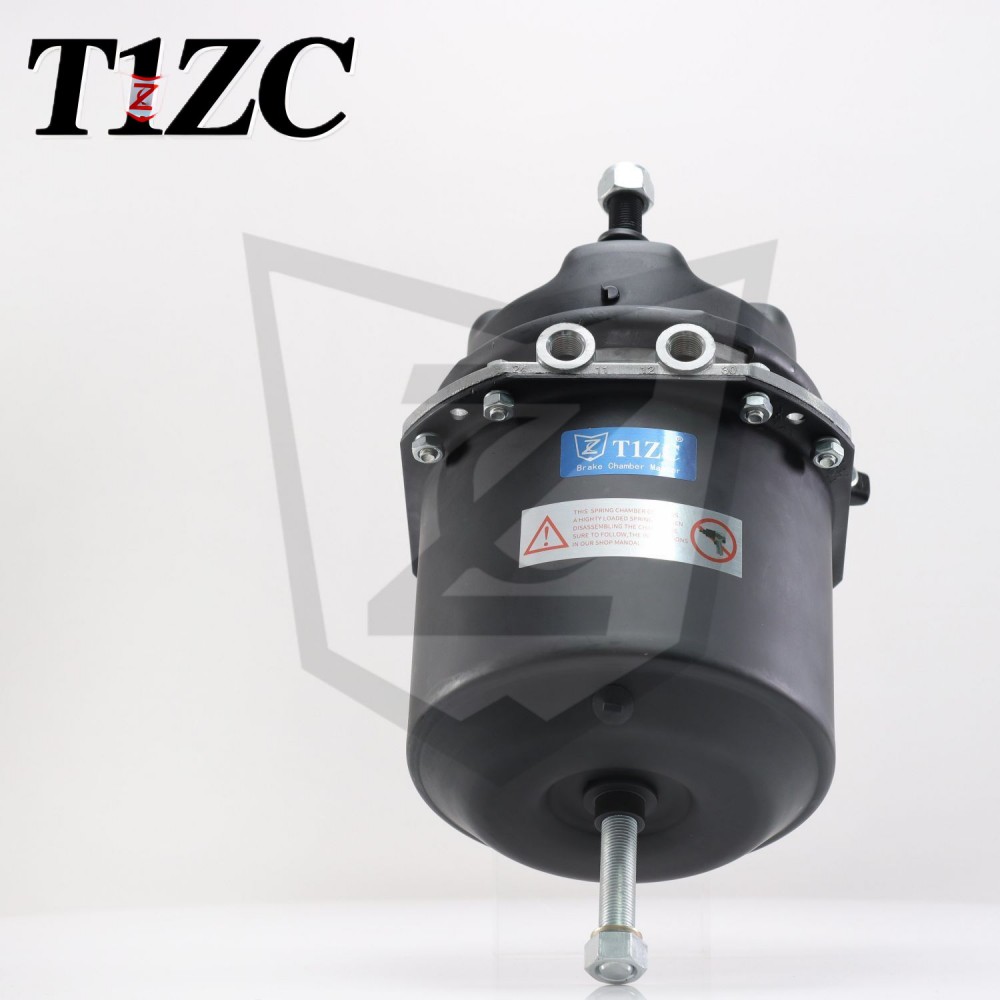
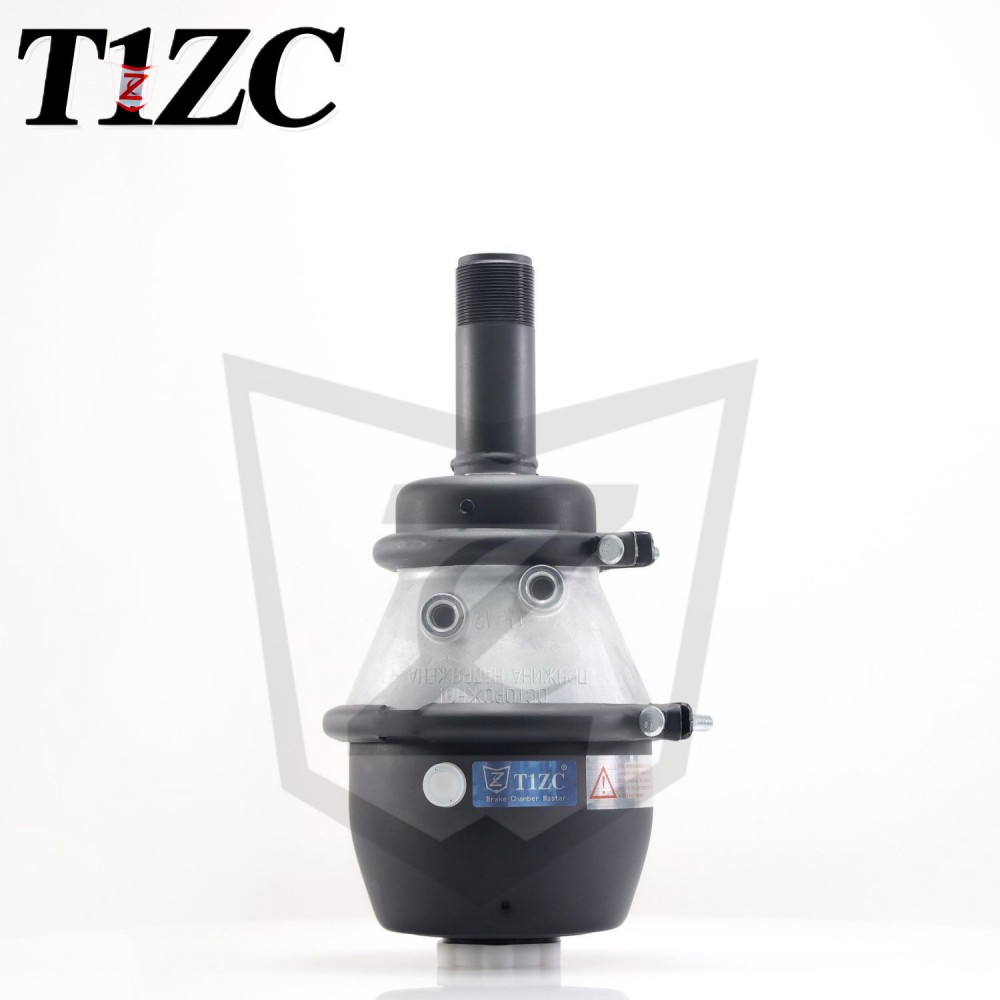
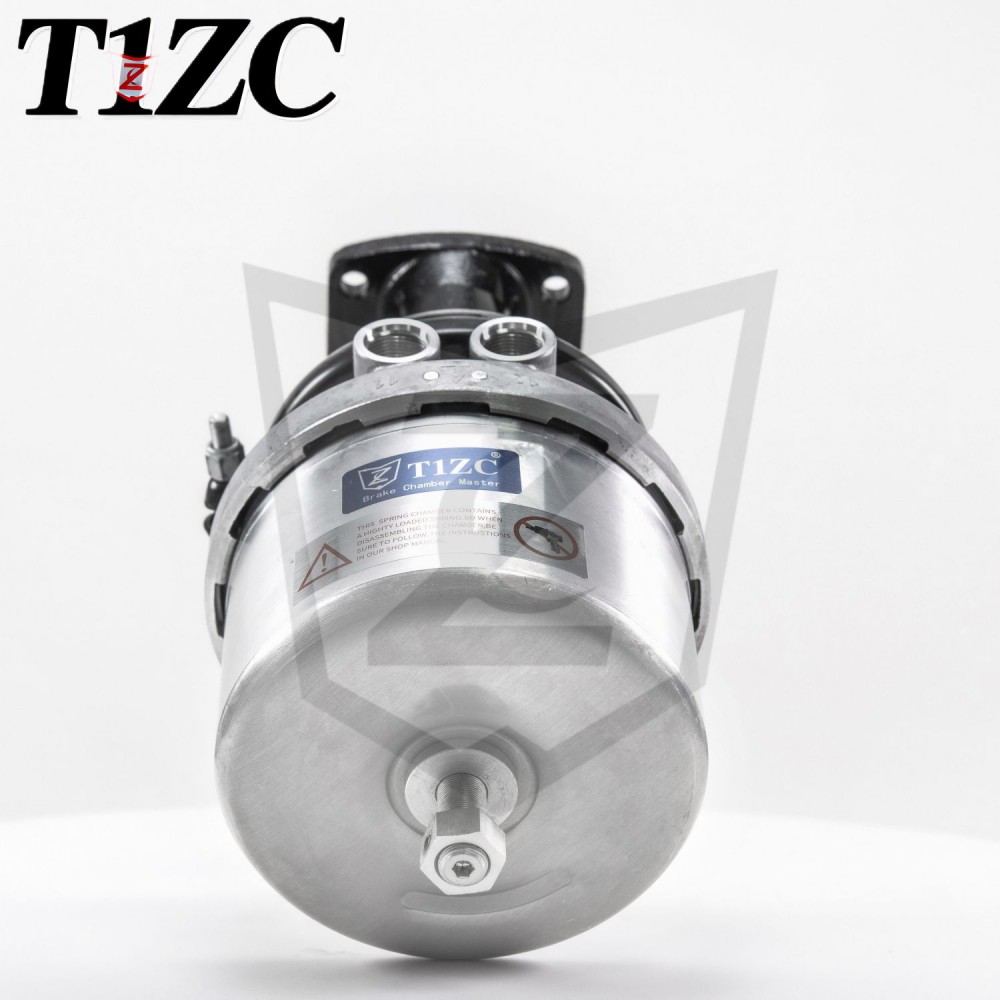
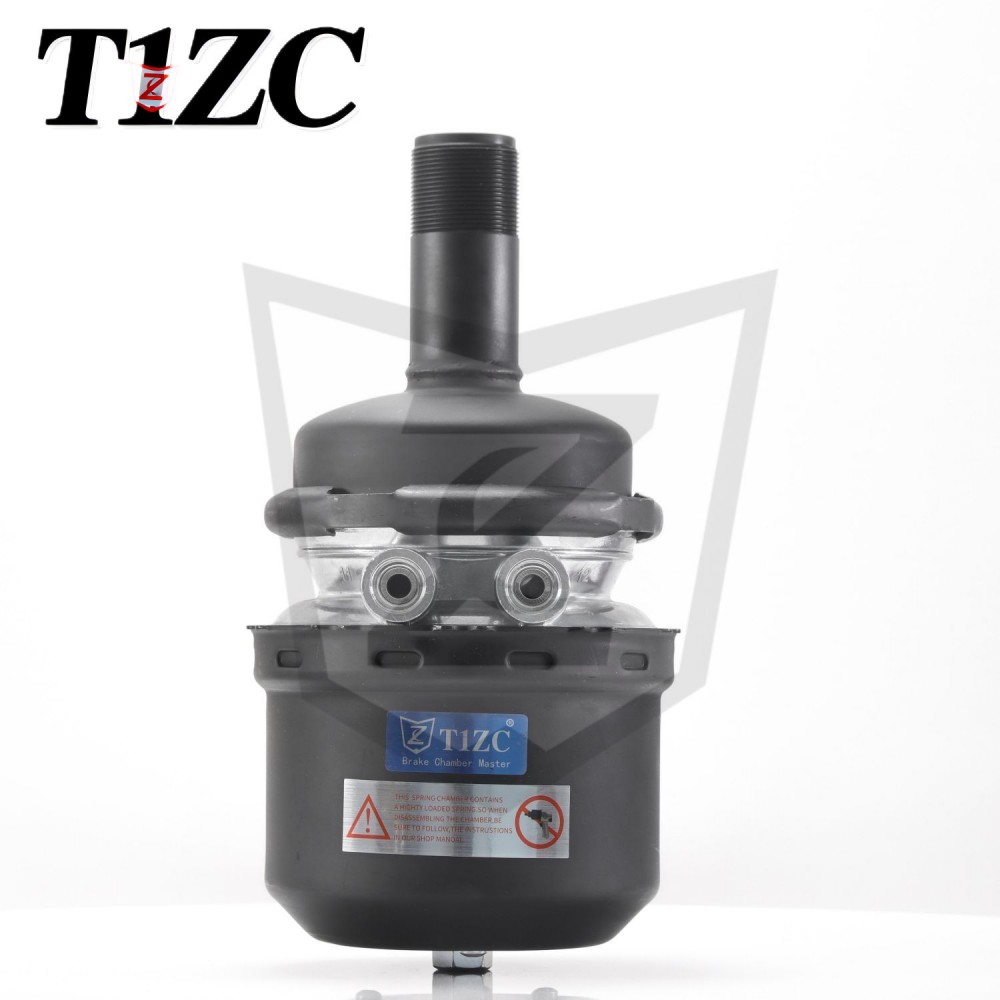
A Wedge Brake Chamber is a critical component in air brake systems used primarily in commercial vehicles, such as trucks and buses. It converts compressed air into mechanical force to activate the braking mechanism, ensuring controlled deceleration and safety. Unlike other brake chamber types, the Wedge Brake Chamber employs a wedge-shaped design to apply force directly to the brake shoes, contributing to its efficiency and compact structure.
Key Components of a Wedge Brake Chamber
The Wedge Brake Chamber consists of several essential parts that work together to facilitate braking. These include:
-
Housing: A durable enclosure that protects internal components from environmental factors.
-
Diaphragm or Piston: A flexible or rigid element that moves in response to air pressure changes.
-
Wedge Mechanism: A tapered component that translates linear motion into force applied to the brake assembly.
-
Return Spring: A spring that retracts the mechanism when air pressure is released, disengaging the brake.
-
Air Inlet: A port for compressed air entry, connected to the vehicle's air supply system.
Each part is engineered to withstand high stress and repetitive use, ensuring consistent operation under varying conditions.
How a Wedge Brake Chamber Functions
The operation of a Wedge Brake Chamber involves a series of mechanical and pneumatic processes. When the brake pedal is pressed, compressed air enters the chamber through the air inlet. This air pressure acts on the diaphragm or piston, causing it to move forward. The motion drives the wedge mechanism into the brake assembly, forcing the brake shoes against the drum or rotor to generate friction and slow the vehicle. Upon release of the air pressure, the return spring restores the components to their original positions, disengaging the brake. This cycle allows for precise control over braking force, enhancing safety in heavy-duty applications.
Step-by-Step Operation Process
-
Air Pressure Application: Compressed air is supplied from the vehicle's reservoir to the Wedge Brake Chamber via the air inlet.
-
Actuation of Internal Components: The air pressure displaces the diaphragm or piston, initiating linear movement.
-
Wedge Engagement: The wedge mechanism is pushed into the brake assembly, converting linear motion into radial force.
-
Brake Application: This force presses the brake shoes against the rotating surface, creating friction to decelerate the vehicle.
-
Pressure Release and Reset: When air pressure is removed, the return spring retracts the wedge, allowing the brake to disengage.
Applications and Benefits of Wedge Brake Chambers
Wedge Brake Chambers are widely used in various sectors due to their design advantages. Common applications include:
-
Commercial trucks and trailers for highway and off-road use.
-
Buses and coaches in public transportation systems.
-
Industrial machinery and construction equipment requiring robust braking solutions.
The benefits of Wedge Brake Chambers stem from their compact size and direct force application, which include:
-
Efficient space utilization, allowing for easier installation in confined areas.
-
Reduced maintenance needs due to fewer moving parts compared to some alternative designs.
-
Consistent performance in diverse temperatures and operating conditions.
-
Enhanced safety through reliable and rapid brake response times.
Maintenance and Safety Considerations
Proper maintenance of Wedge Brake Chambers is essential for optimal performance and longevity. Key practices involve:
-
Regular inspections for signs of wear, such as cracks in the housing or diaphragm.
-
Checking air lines for leaks and ensuring connections are secure.
-
Lubricating moving parts as per manufacturer guidelines to prevent corrosion.
-
Testing the return spring functionality to verify complete brake release.
Safety protocols emphasize the importance of using certified components and following industry standards, such as those set by transportation authorities, to prevent failures and ensure operational integrity.


 EN
EN  English
English Português
Português